This abstract was presented today, April 8th at the 2019 Association for Research in Vision and Opthalmology (ARVO) meetings in Vancouver, Canada by Selena Wirthlin, Crystal L. Sigulinsky, James R. Anderson, Daniel P. Emrich, Christopher Rapp, Jeebika Dahal, Rebecca L. Pfeiffer, Kevin D. Rapp, Jia-Hui Yang, Carl B. Watt, Robert E. Marc and myself.
Full resolution version here.
Purpose
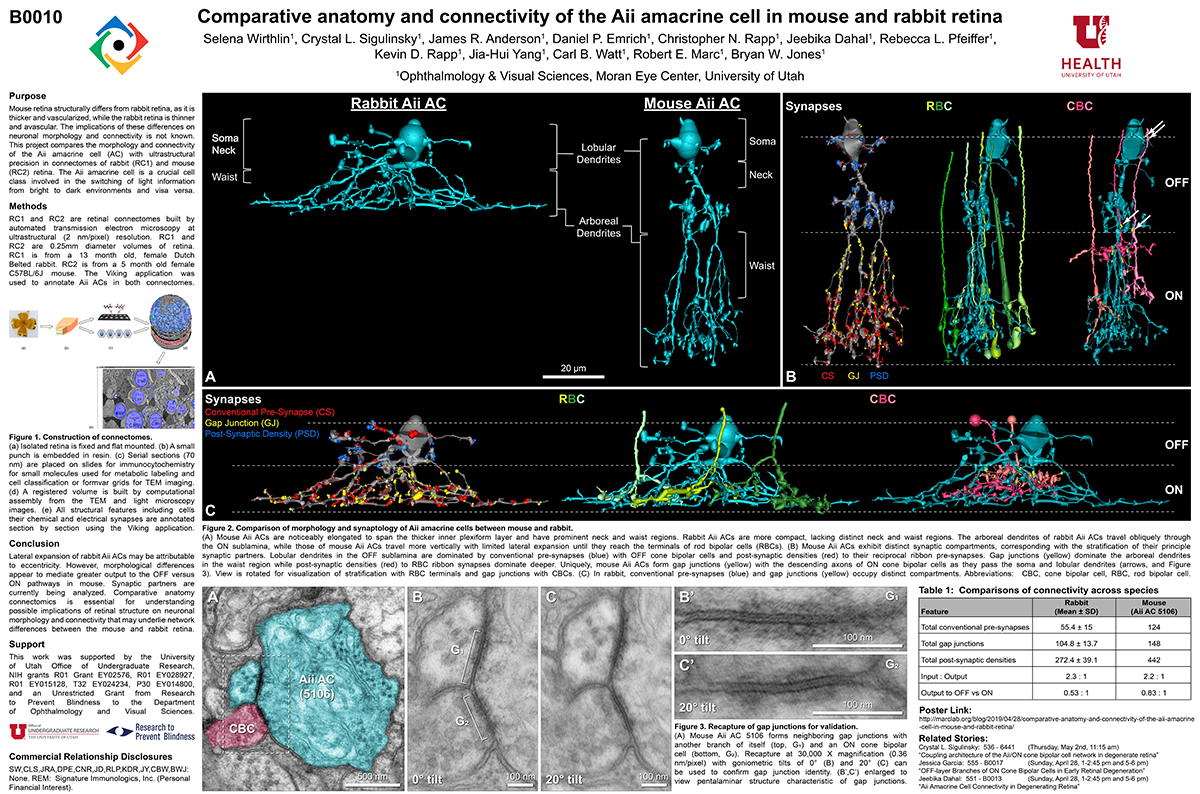
Mouse retina structurally differs from rabbit retina, as it is thicker and vascularized, while the rabbit retina is thinner and avascular. The implications of these differences on neuronal morphology and connectivity is not known. This project compares the morphology and connectivity of the Aii amacrine cell (AC) with ultrastructural precision in connectomes of mouse (RC2) and rabbit (RC1) retina.
Methods
RC1 and RC2 are connectomes built by automated transmission electron microscopy at ultrastructural (2 nm/pixel) resolution. RC1 and RC2 are 0.25mm diameter volumes of retina. RC1 is from a 13 month old, female Dutch Belted rabbit. RC2 is from a 5 month old female C57BL/6J mouse. The Viking application was used to annotate Aii ACs in both connectomes.
Results
Mouse Aii ACs are noticeably elongated to span the thicker inner plexiform layer (IPL) and have a prominent neck region. Lobular appendages of Aii ACs in both species extend thin stalks from the soma, neck and proximal arboreal dendrites in the OFF sublamina, predominantly forming reciprocal synapses with OFF cone bipolar cells (BCs). In rabbits, multiple arboreal dendrites emerge from the base of the neck, branch and travel obliquely through the ON sublamina, and form gap junctions with ON cone BCs, neighbor Aii ACs, and itself. They extend laterally at the base of the IPL, collecting ribbon input from rod BCs. In contrast, mouse arboreal dendrites stem from a single primary dendrite that branches as it travels vertically through the IPL without self-branch interaction, terminating at variable depths that align with the more broadly ramified axon terminals of rod BCs. Conventional synapse to gap junction ratios reveal greater output in the OFF vs ON layer in mouse compared to rabbit. Notably, mouse Aii ACs form gap junctions with the descending axons of ON cone BCs as they pass its soma, in contrast to rabbit, where gap junctions do not form at contacts proximal to ON cone BC axon terminals.
Conclusions
Lateral expansion of rabbit Aii ACs may be attributable to eccentricity. However, morphological differences appear to mediate greater output to the OFF versus ON pathway in mouse. Synaptic partners are currently being analyzed. Comparative anatomy connectomics is essential for understanding possible implications of retinal structure on neuronal morphology and connectivity that may underlie network differences between the mouse and rabbit retina.